Contents
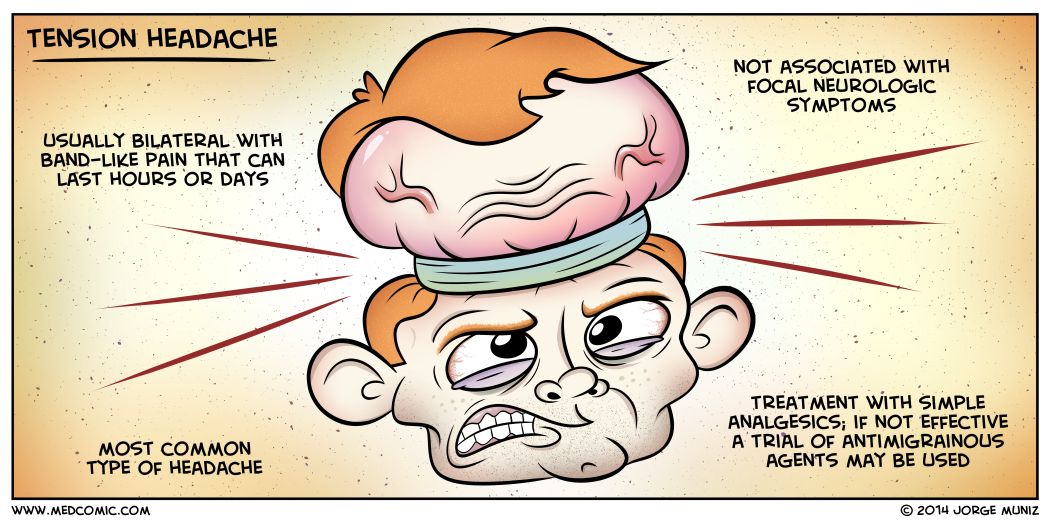
Recurrent episodes of headache lasting minutes to weeks.
- M/C type of primary headache (69%)
Classification
- Infrequent episodic TTH
- Associated with pericranial tenderness
- Not associated with pericranial tenderness
- Frequent episodic TTH
- Associated with pericranial tenderness
- Not associated with pericranial tenderness
- Chronic TTH
- Associated with pericranial tenderness
- Not associated with pericranial tenderness

Aetiology
- ♀ >> ♂
Precipitating factors:
- Stress
- Lack of sleep
- Not eating on time
Clinical features
Headache:
- Pressing/tightening in quality
- Mild-to-moderate intensity
- Bilateral in location
- Does not worsen with the routine physical activity (and does not stop daily activities)
- Associated features:
- Photophobia/phonophobia present
Nausea & vomitingusually absent- No sleep disturbances


Diagnosis
International Classification of Headache Disorders (ICHD-3) criteria:

Fundal examination:
- Papilloedema
Management
Non-pharmacological management:
- Physical therapy (M/C):
- Improvement of posture
- Relaxation
- Exercise programs
- Hot and cold packs
- Ultrasound, and electrical stimulation
- Craniocervical training
- Psychologic therapy:
- Relaxation training
- EMG biofeedback
- Cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT)
Pharmacotherapy:
- Acute TTH: Analgesics and NSAIDSs (mainstays in acute therapy)
- Chronic TTH: Amitriptyline (tricyclic antidepressant): M/effective